1. Überblick über die Branche der öffentlichen Ladestationen
Die Ladestation für Elektrofahrzeuge ist eine wichtige Infrastruktur im Zeitalter der neuen Energiefahrzeuge. Ladestationen für neue Energiefahrzeuge beziehen sich auf die Geräte, die Ladedienste für neue Energie-Elektrofahrzeuge anbieten. Sie werden an öffentlichen Orten wie öffentlichen Gebäuden, Parkplätzen, Einkaufszentren, Ladestationen für Betriebsfahrzeuge und an privaten Orten wie Wohnsiedlungen installiert.
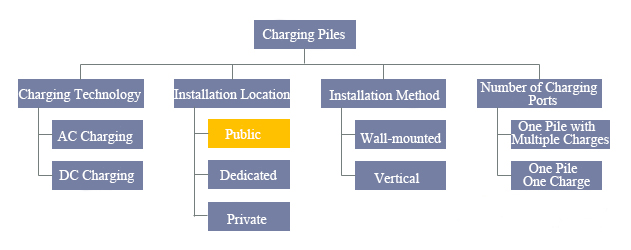
Gemeinsame Klassifizierungen von Ladestationen:
Je nach den Installationsbedingungen handelt es sich dabei hauptsächlich um vertikale Ladestationen und wandmontierte Ladestationen. Entsprechend den Servicezielen werden sie hauptsächlich in öffentliche Ladestationen, spezielle Ladestationen und private Ladestationen unterteilt. Unterteilt nach der Anzahl der Ladeschnittstellen, hauptsächlich unterteilt in eine Station und mehrere Ladestationen. Unterteilt nach Ladetypen, hauptsächlich unterteilt in AC-Ladestationen und DC-Ladestationen.
2. Aktuelle Situation der globalen öffentlichen EV-Ladestationen Industrie
In den letzten Jahren ist die Zahl der öffentlichen Ladestationen weltweit rapide gestiegen. Und der weltweite Bestand an öffentlichen Ladestationen wird im Jahr 2020 1,308 Millionen Einheiten erreichen. Darunter befinden sich 386.000 Schnellladestationen (Leistung > 22 kW). Und die Zahl der Langsamladestationen (Leistung ≤ 22 kW) beträgt 922.000.
2.jpg)
Ähnlicher Bericht: China Public Charging Station Industry Market Panorama Assessment and Development Strategic Planning Report 2022-2027 veröffentlicht von China Economic Research Institute
3. Aktuelle Situation der öffentlichen Ladestationen in China
Die Verkäufe und Bestände von Fahrzeugen mit neuer Energie in China steigen rapide an, aber die Fortschritte beim Bau der Infrastruktur können nicht mit dem Expansionstempo Schritt halten. Bis Ende 2021 werden in China 7,84 Millionen Fahrzeuge mit neuer Energie betrieben, 59 % mehr als im Vorjahr, und 3,521 Millionen Fahrzeuge verkauft, 157,51 % mehr als im Vorjahr.
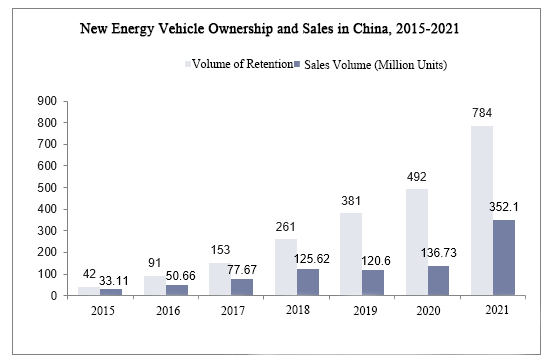
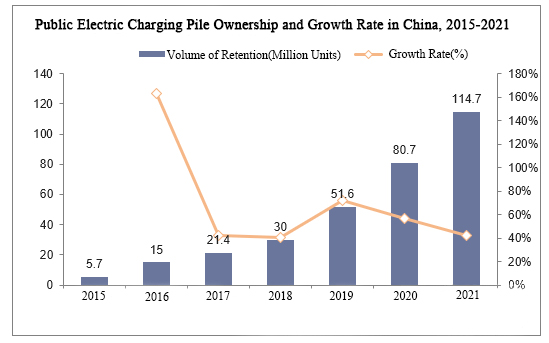
Das Aufladen an Ladestationen ist die gängigste Methode, um die Energie von Fahrzeugen mit neuer Energie in China wieder aufzufüllen. Und im Jahr 2021 wird die Zahl der öffentlichen Ladestationen in China 1,147 Millionen betragen, was einem Anstieg von 42,13 % gegenüber dem Vorjahr entspricht.
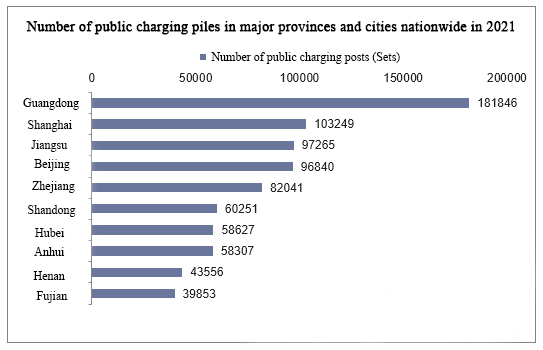
Das Baugebiet für die öffentliche Ladeinfrastruktur ist stärker konzentriert. 2021 Die Provinz Guangdong hat 181.800 öffentliche Ladestationen und liegt damit weit vor den anderen Provinzen und Städten. Gefolgt von Shanghai mit 103.200 öffentlichen Ladestationen. Die Provinz Jiangsu und Peking liegen mit 97.300 bzw. 96.800 öffentlichen Ladestationen dicht beieinander.
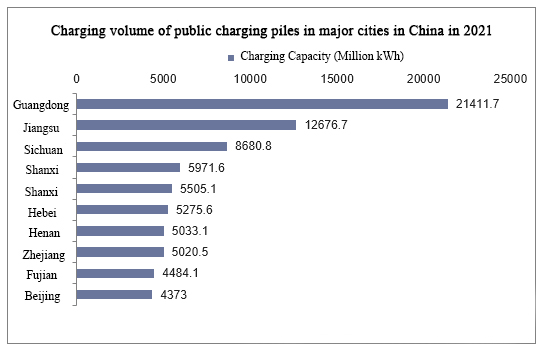
Was das Ladevolumen betrifft, so ist die Provinz Guangdong mit 214 Millionen kWh die Provinz und Stadt mit den meisten öffentlichen Ladestationen in China im Jahr 2021; an zweiter Stelle steht die Provinz Jiangsu mit 127 Millionen kWh und an dritter Stelle die Provinz Sichuan mit 0,87 Milliarden kWh.
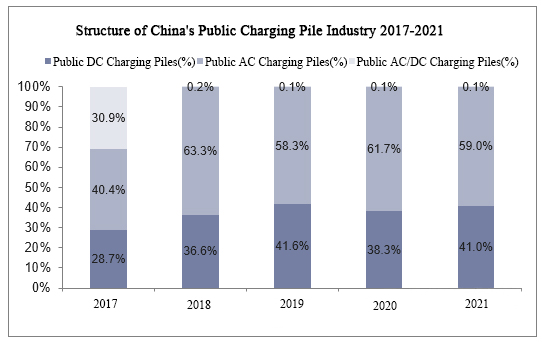
Seit 2018 werden die öffentlichen Ladestationen in China von zwei Kategorien dominiert: Gleichstrom-Ladestationen und Wechselstrom-Ladestationen, und der Anteil der Wechselstrom- und Gleichstrom-Ladestationen ist sehr gering. Von 2017 bis 2019 stieg der Anteil der DC-Ladestationen von 28,7 % auf 41,6 %, was einen rasanten Anstieg bedeutet. Von 2019 bis 2021 ist das Verhältnis zwischen Gleichstrom- und Wechselstrom-Ladestationen relativ stabil. Der Anteil der AC-Ladestationen wird bei etwa 60% bleiben. Und der Anteil der DC-Ladestationen wird bei etwa 40% bleiben.
4. Wettbewerbsmuster der Branche der öffentlichen Ladestationen
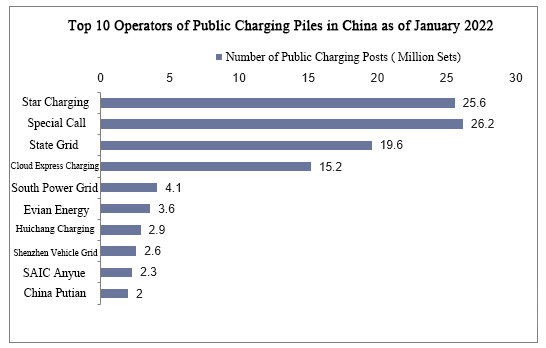
Die Konzentration der Betreiber öffentlicher Ladestationen ist hoch. Im Januar 2022 gibt es in China 13 öffentliche Ladestationen, die von Betreibern betrieben werden, wobei die Zahl der öffentlichen Ladestationen 10.000 Einheiten übersteigt. Sie sind Star Charging, Special Call, State Grid, Cloud Fast Charging, Southern Power Grid, Yiwei Energy, Hui Charging, Shenzhen Vehicle Grid, SAIC Anyue, China Putian, Wanma Aichong, Wancheng Wanchong und Hengtong Dingchong.
Auf diese 13 Betreiber entfallen 93 % der Gesamtzahl, auf die übrigen Betreiber 7 % der Gesamtzahl.