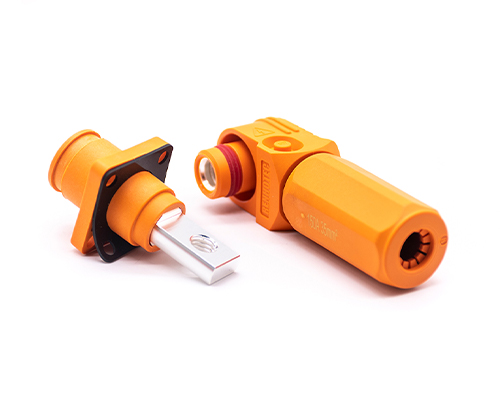
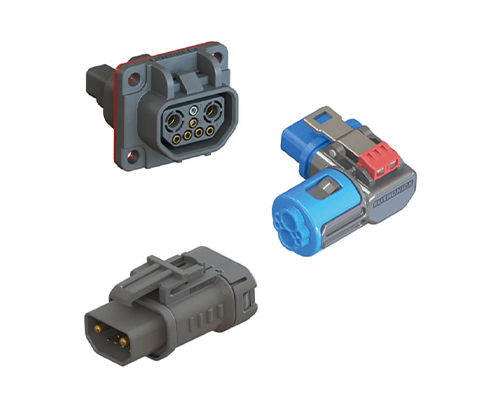
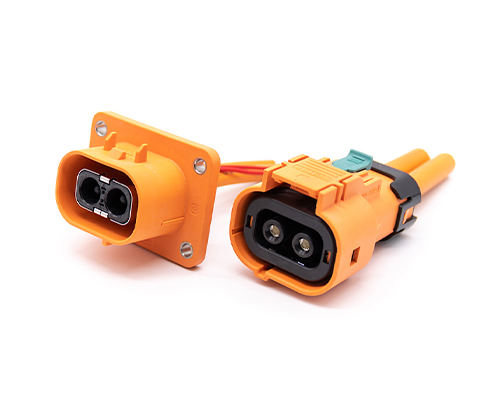
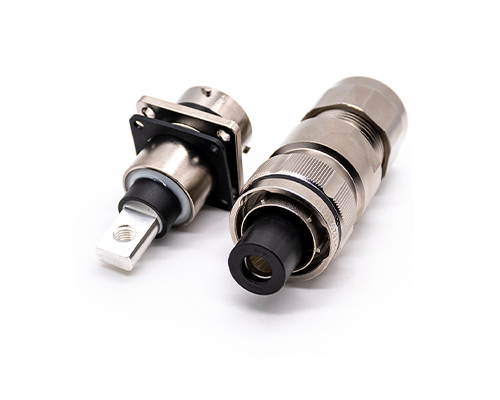
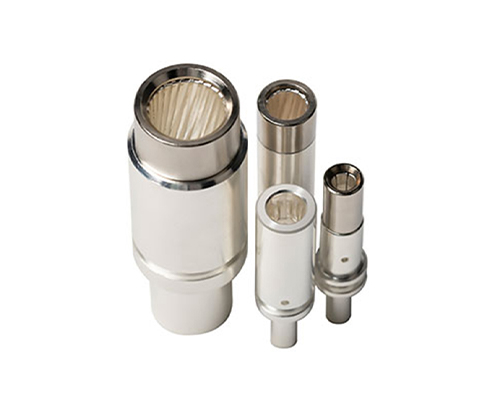
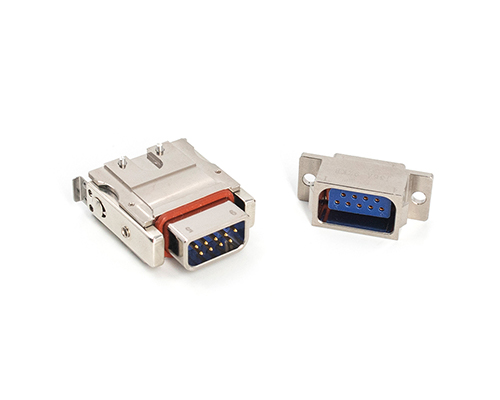
High Voltage Connector
High Voltage Connectors are widely used in EV power systems, renewable energy installations, and industrial high-voltage circuits. Renhotec’s series drives the building of efficient, safe, and sustainable electrical ecosystems, meeting current technological demands.
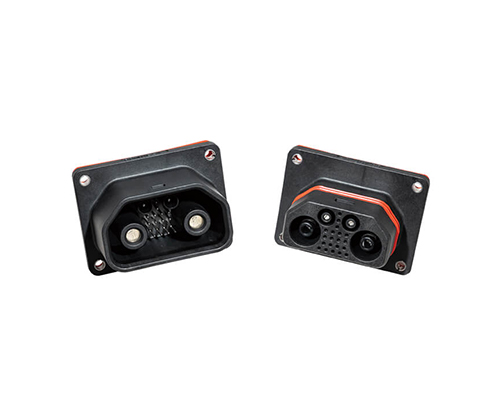
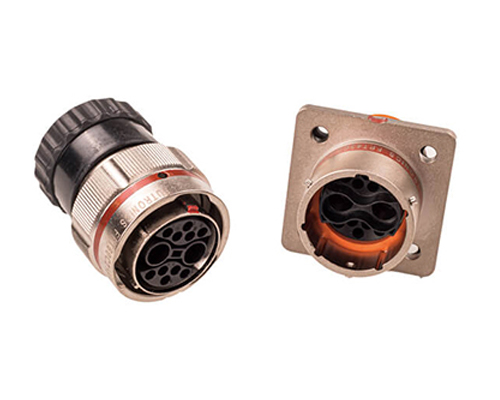
High Voltage Signal Connector
Renhotec, as a professional supplier, offers a comprehensive range of these Signal Transmission Connector products. Whether it is the high-reliability applications of the metal series or the wide adaptability of the plastic series in consumer electronic products, Renhotec can provide customers with high-quality options to meet the diverse requirements of signal transmission connections in different industries and scenarios.
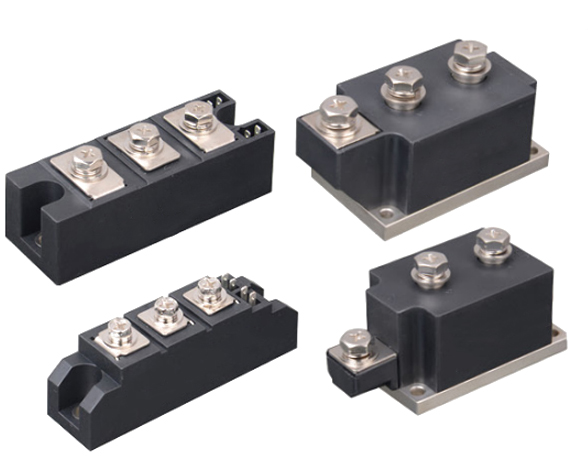
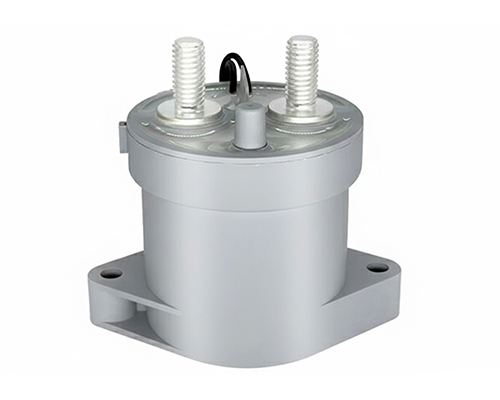
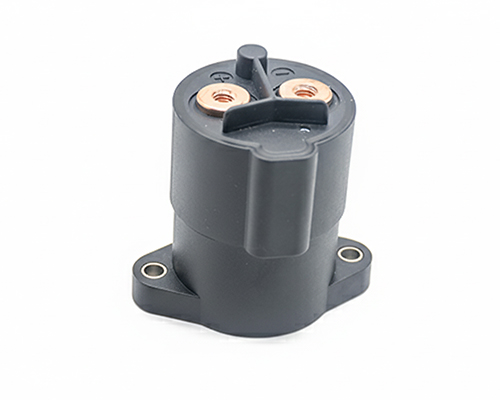
High Voltage DC Contactor
Renhotec, active in electrical components, offers High Voltage DC Contactors in Epoxy Resin Sealing and Ceramic Sealing variants, with a 20A – 1000A current range. The Epoxy Resin Sealing one is cost-effective and protective. The Ceramic Sealing variant excels in thermal stability and insulation. They’re widely used in EV charging, renewable energy grid, and industrial high-voltage DC power distribution for reliable circuit control and current interruption, providing comprehensive solutions for multiple sectors.
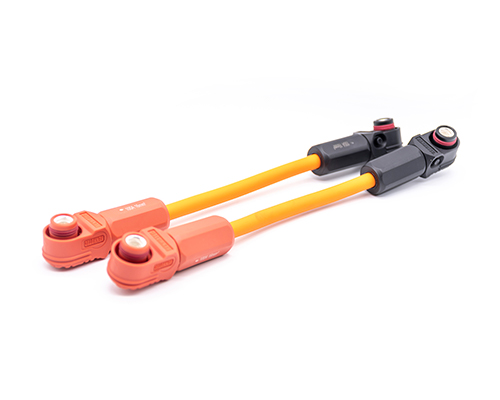
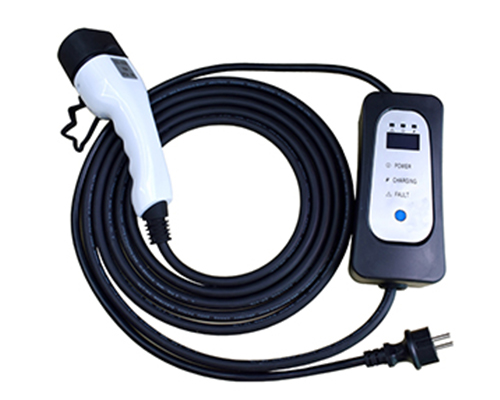
High Voltage EV Cable
Renhotec EV Cable, crafted with top-notch conductive materials and meticulously engineered insulation, showcases outstanding impedance control and voltage-withstanding properties. Its design combines flexibility and durability to meet a wide array of installation needs. This cable is widely utilized in grid interconnections, large-scale industrial power supply systems, and high-voltage renewable energy projects, enabling smooth and efficient power transmission.
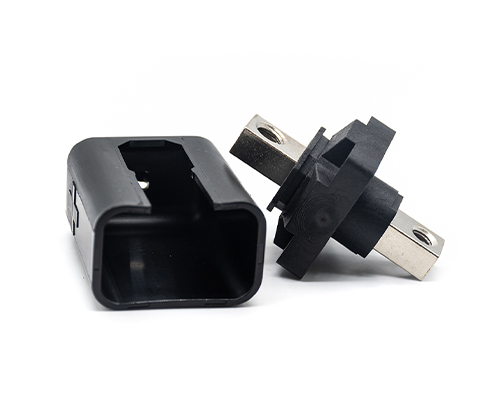
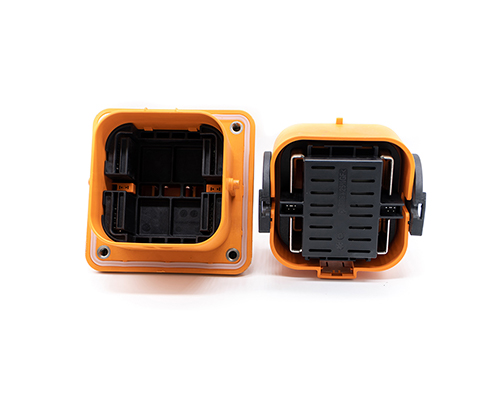
Power Drawer Connector
Renhotec’s Drawer Connector, available in 4 – 37 cores, features a compact and flexible design. It can provide reliable electrical connections varying in complexity. The various core options make it suitable for a wide variety of small electrical appliances and drawer-mounted devices. It enables efficient power and signal transfer, facilitating the operation and integration of internal components, and is a viable option in the connector market.
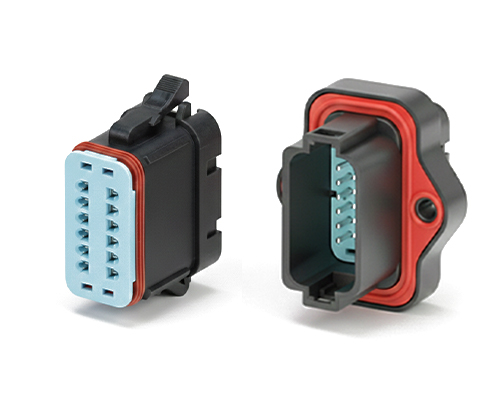
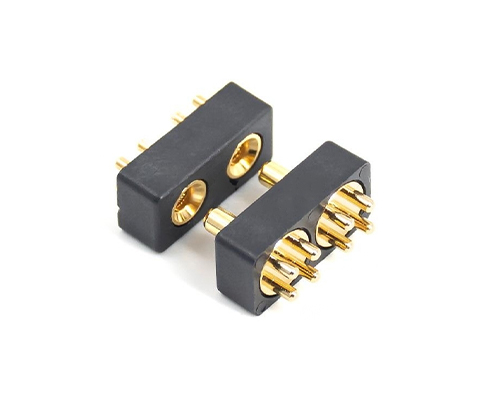
Floating Board to Board Connector
The Floating BTB Connector is a key component designed to achieve a reliable electrical connection between two circuit boards.
It is widely used in various electronic devices that require high connection stability and signal integrity, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and industrial control equipment etc., to build a stable and efficient communication bridge between circuit boards in complex electronic systems.
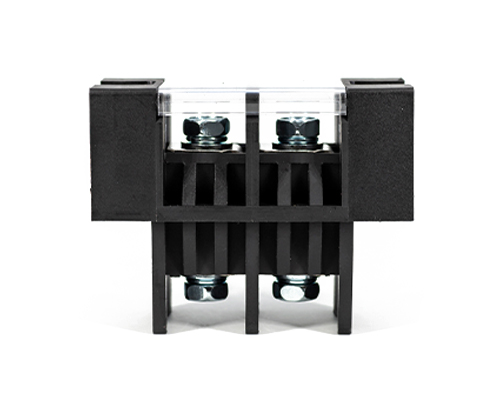
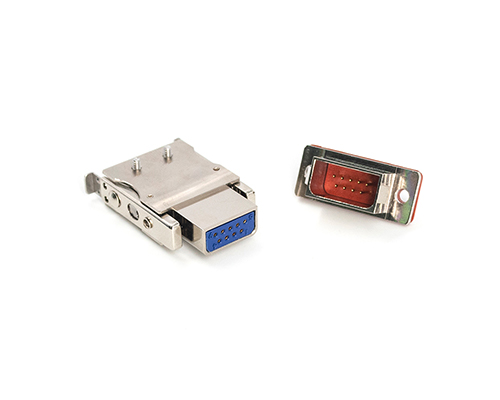
Rectangular Connector
The Rectangular Connector is widely used in consumer electronics (such as computers, TVs, game consoles, etc.), industrial control equipment, communication equipment, and automotive electronics. With its reliable connection performance, diverse specifications, and relatively convenient plug-in and unplug operations, it has become an indispensable component in various electronic and electrical applications.
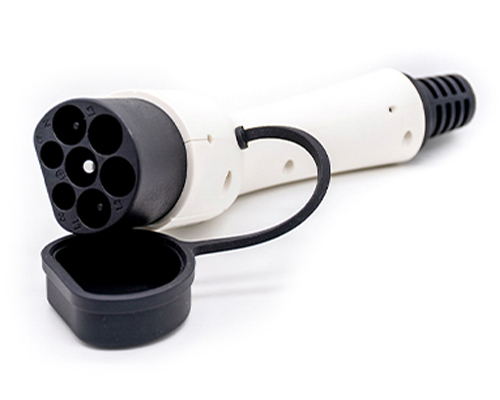
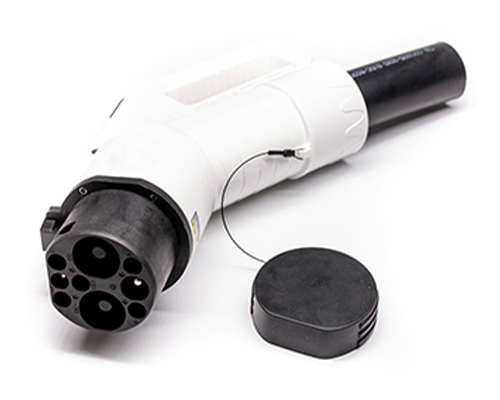
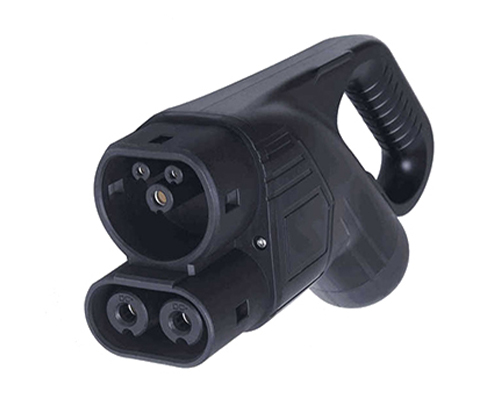
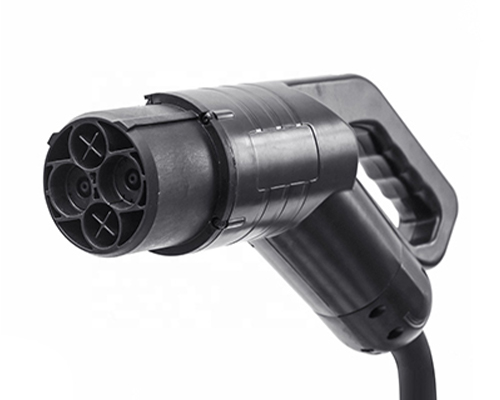
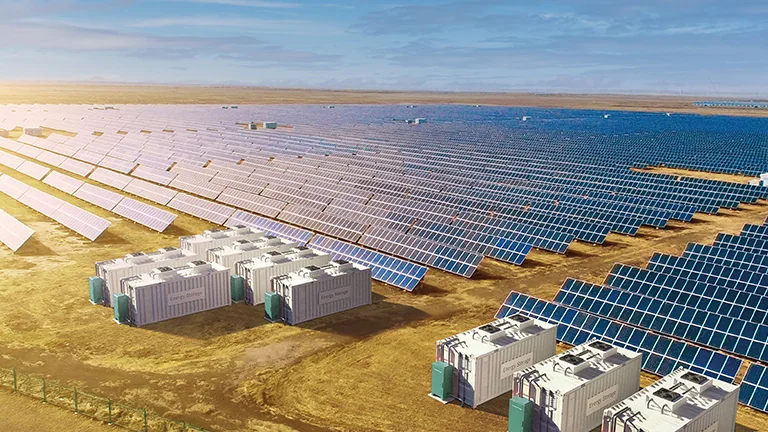

































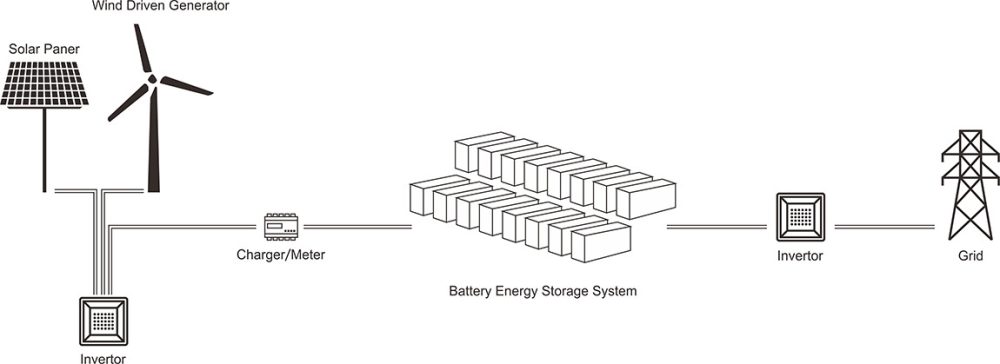
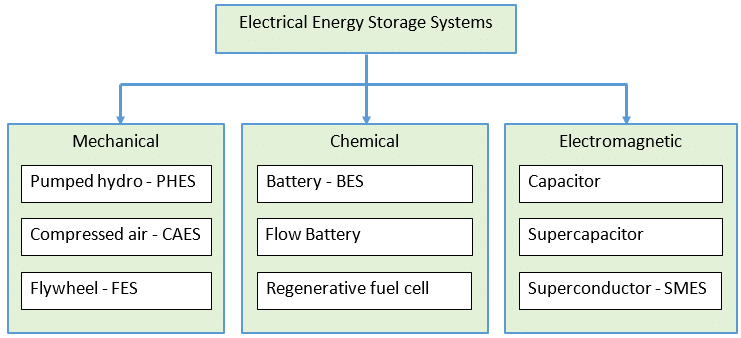







Energy storage systems are essential for ensuring the stability and reliability of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. ?? As these intermittent sources become more widespread, technologies like batteries, flywheels, and compressed air storage are helping to balance supply and demand, improve grid performance, and support energy independence. ?⚡ It’s exciting to see how innovations in energy storage will continue to optimize power systems and make renewables more efficient and cost-effective. With further advancements, we’ll move even closer to a greener and more sustainable energy future! ?
Energy storage systems are essential for balancing grid supply and demand, particularly with renewable energy sources like solar and wind. These systems store excess energy when demand is low and release it during peak times, improving grid reliability. Technologies like batteries, flywheels, and pumped storage are key to this process, supporting renewable energy integration and ensuring a stable power supply. As storage technology evolves, it will play a crucial role in building a sustainable energy future.